UM-LISA: guided wave solver for solid structures
One field of research in Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) is relevant to guided wave modeling and simulation. An in-house code has been developed at the University of Michigan, with abundant features for wave simulation such as non-reflective boundary (NRB) techniques, piezoelectric coupled, contact dynamics, multiple GPU parallelization, etc. The code is running on a multiple-GPU platform and is demonstrated to be much more efficient than commericial Finite Element software.
The algorihtm we adopted is Local Interacation Simulation Approach (LISA), a finite difference solver proposed by P. P. Delsanto around 1997. The solver incoporated a sharp interface model (SIM) to deal with discontinuity at interfaces, and ensure both the continuity of displacements and stresses.
All features that are currently available in UM-LISA is shown below
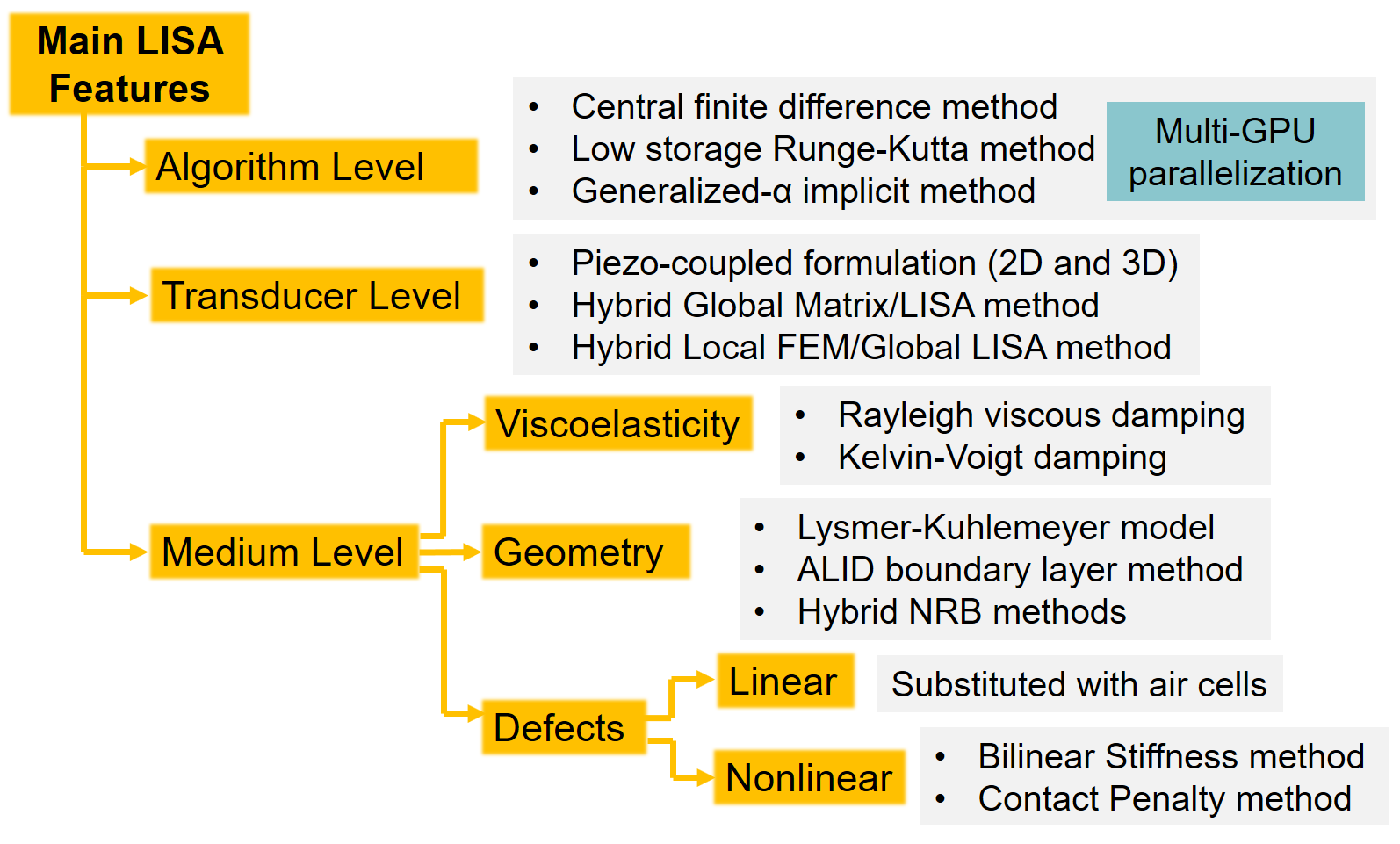
For more information about the algorithm and features, please check the following references.
References
-
Raghavan, A. and Cesnik, C. E. S., “Review of guided-wave structural health monitoring,” Shock Vib. Dig. 39(2), 91–114 (2007).
-
Delsanto, P. P., Schechter, R. S. and Mignogna, R. B., “Connection machine simulation of ultrasonic wave propagation in materials III: the three-dimensional case,” Wave Motion 26(1), 329–339 (1997).
-
Nadella, K. S. and Cesnik, C. E. S., “Numerical simulation of wave propagation in composite plates,” Proc. SPIE, 83480L (2012).
-
Nadella, K. S. and Cesnik, C. E. S., “Piezoelectric coupled LISA for guided wave generation and propagation,” Proc. SPIE, 86951R (2013).
-
Zhang, H. and Cesnik, C. E. S., “A hybrid non-reflective boundary technique for efficient simulation of guided waves using local interaction simulation approach,” Proc. SPIE, 98050U (2016).

